

RAPID PROTOTYPING: SKETCHING
—Task two·viedo one
The video shows how to go from concept to actual product through these three
methods—Sketching &
Paper Prototyping: Rapidly create prototypes by hand drawing or printing
Sketching and paper prototypes are an indispensable first step in the design process.
They can
quickly promote project development in a simple way and lay the foundation for subsequent
digital and native prototypes. This approach emphasizes "speed first" and the core is to capture
the design concept and quickly verify the initial idea
Low cost and high efficiency
Making paper prototypes only requires paper and pen, is extremely low-cost and does not require
complex tools. Designers can quickly generate multiple design options for comparison
The visual language of culture
Many of her designs draw directly from her multicultural background, such as the intricate
patterns
and use of color found in Asian design aesthetics. By incorporating global cultural symbols, her
work is more diverse and inclusive
High flexibility
Modifications are simple, and designers can adjust or add new functional modules on paper at any
time
Intuitiveness
Hand-drawn sketches can present the design structure in its simplest form, making it easier for
team members to understand the design concept
Early validation and collaboration
In the early stages of a project, sketches can facilitate team discussions and quickly gather
feedback
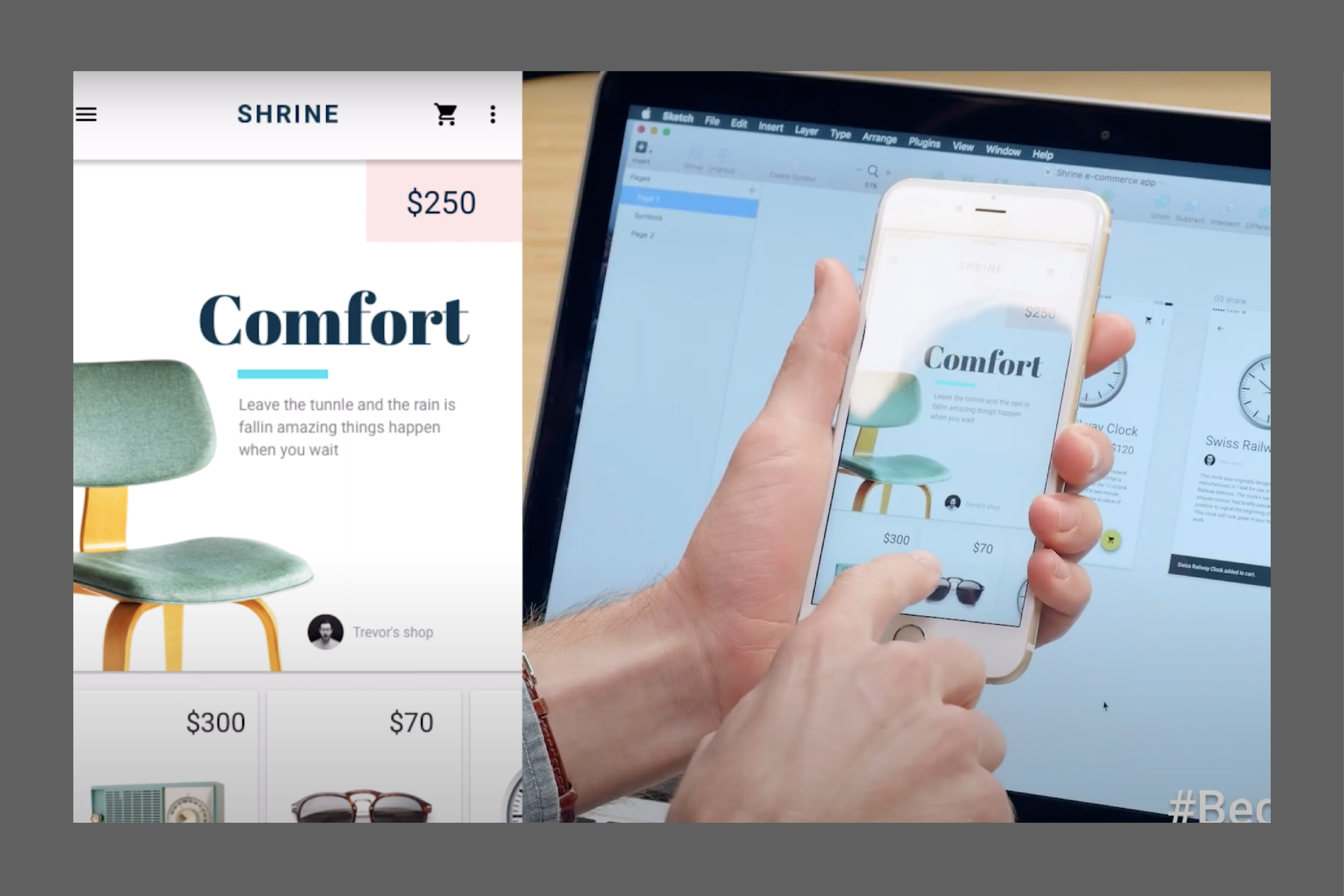
RAPID PROTOTYPING: DIGITAL
—Task two·viedo two
The video shows how to go from concept to actual product through these three methods—Digital
Prototyping: Use design tools to create more detailed interactive prototypes and
simulate the
functions and layout of the interface
Digital prototyping is an important link in the design process, finding a balance between
visual
representation and interactive testing. Compared with paper prototypes, digital prototypes can
present design ideas more accurately, helping teams quickly identify problems and optimize user
experience
Greater visual accuracy
Digital prototypes provide a more refined visual representation than paper prototypes and can
show details such as interface layout, color, and fonts, making the design closer to the actual
effect
Highly interactive
Designers can use tools to add dynamic effects to simulate real user experience
Easy to test and share
Digital prototypes can be easily shared with team members and users, making them suitable for
remote collaboration and testing. At the same time, it can record user feedback in real time to
help optimize the design
Iterate quickly
With tools, designers can quickly adjust and update designs, eliminating time spent redrawing
RAPID PROTOTYPING: NATIVE
—Task two·viedo three
The video shows how to go from concept to actual product through these three methods—Native
Prototyping: A high-fidelity prototype that runs on an actual device, usually made using
real
code or frameworks, and is close to the final product
Native prototype is the final stage of product design, pursuing high fidelity and
technical
feasibility verification. It can present a complete user experience, ensure that the design has
been fully verified before development, and reduce the cost of later changes
High fidelity
The native prototype not only looks close to the final product, but also has complete
interactive functions and dynamic effects, which can truly simulate the user experience
Real device testing
Designers and development teams can test on the target device to ensure functionality and
performance in a real-world environment
Verify technical feasibility
By using real code, the team can discover difficulties and potential problems in technical
implementation in advance, paving the way for subsequent development work
Demonstration and persuasion
Native prototypes are suitable for showing to customers, investors, or decision-makers because
they are closer to finished products and can convey the value of the design more convincingly
USEFUL RESOURCE: WEBSITE
—A complete guide to prototyping
Clear Explanation of Prototype Fidelity
The guide distinguishes between low-fidelity prototypes, which are inexpensive and ideal
for
quick testing, and high-fidelity prototypes, which closely resemble the final product
with
detailed visuals and interactions
Overview of Prototyping Methods
The guide outlines various methods such as paper prototypes, linked wireframes, and digital
prototypes. Each method is explained with its purpose, advantages, and limitations, making it
practical for real-world applications
Emphasis on Iteration and User Testing
Prototyping is presented as an iterative process, enabling designers to refine ideas and resolve
usability issues effectively through continuous feedback, especially during user testing
Applicability Across Design Stages
The guide demonstrates how prototyping contributes to every stage of product design, from early
brainstorming to presenting high-fidelity designs to stakeholders, emphasizing its significance
throughout the product development lifecycle
liushuyan_uk2024@163.com