Rapid Prototyping: Sketching | Google for Startups
1. Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is the process of turning ideas into tangible forms
to communicate and test them effectively. It emphasizes that the
fidelity of the prototype should match the fidelity of the thinking.
Sketching and paper prototyping are fundamental methods, ranging from
simple outlines to detailed, high-fidelity sketches that include
buttons, images, and colors. Paper prototyping focuses on key user
interactions, the purposeful use of colors, and the exploration of
elevation and shadows to simulate real-world scenarios. Digital tools
further enhance this process by allowing designers to visualize and
validate user flows and interactions through wireframes, rapid
sketches, and detailed designs. This combination of tools ensures
better communication of ideas and more effective validation.
Rapid Prototyping: Digital | Google for Startups
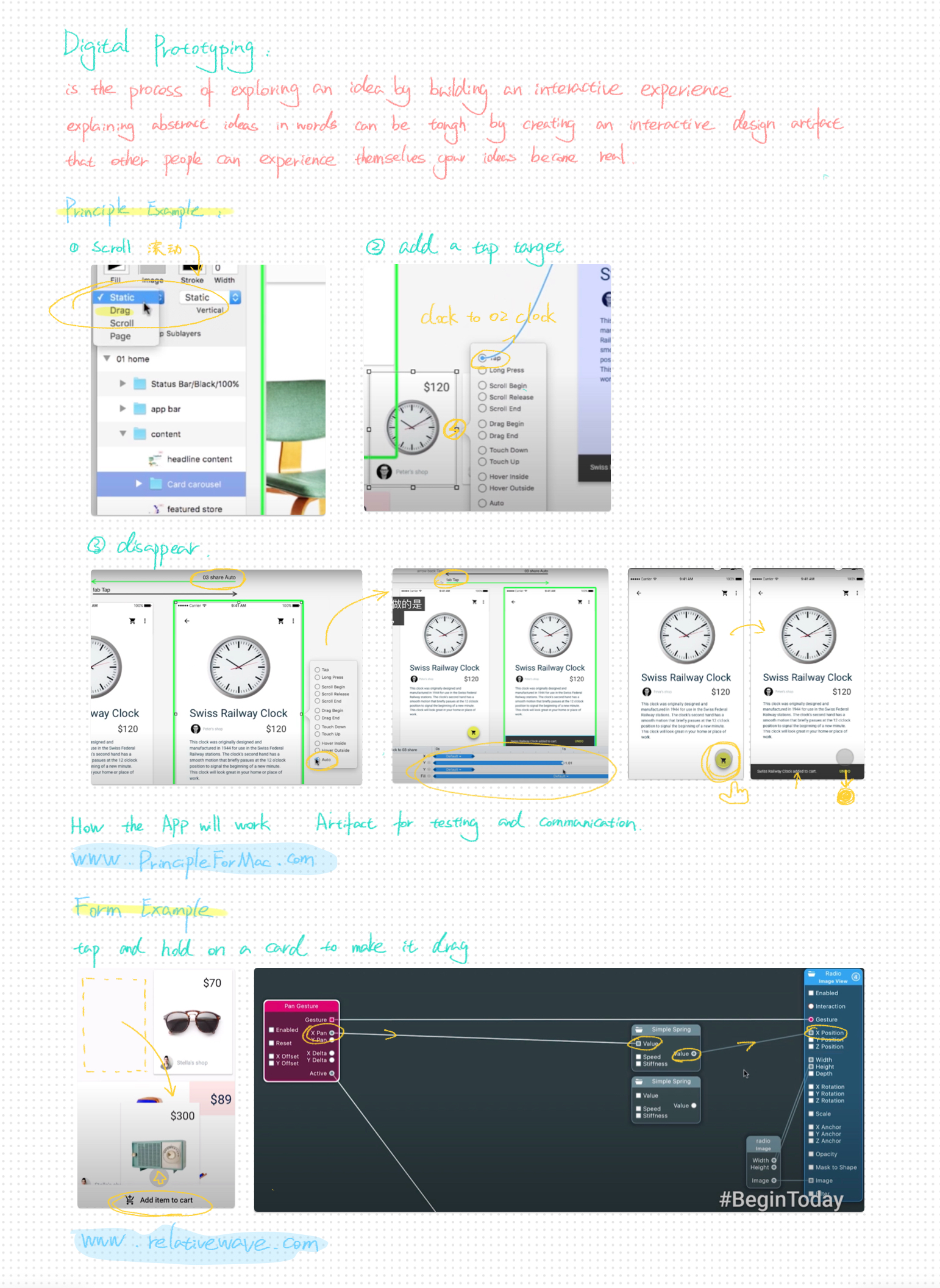
2. Digital Prototyping-image"
Digital prototyping involves creating interactive experiences to
explore and communicate ideas more vividly. Instead of explaining
abstract concepts with words, designers can build prototypes that
allow users to interact directly, providing a better understanding of
the intended experience. Tools like Principle for Mac enable designers
to simulate app functionalities such as scrolling, adding tap targets,
and creating smooth transitions. These prototypes serve as artifacts
for testing and presenting ideas, making them a valuable resource for
gathering feedback. For example, using animations and interactive
components helps demonstrate how an app would function in a real-world
setting. This approach ensures a clear and detailed visualization of
user interactions, making it easier to refine the design.

Rapid Prototyping: Native | Google for Startups
3. Native Prototyping
Native prototyping leverages advanced technology to create more
realistic prototypes by utilizing platforms, libraries, frameworks,
and device-specific sensors. Technologies such as Java, Python, and
Swift, along with devices like smartphones and Arduino, allow
designers to explore features like gyroscopes, cameras, microphones,
and GPS. This process follows an iterative approach: design,
prototype, test, validate, and refine. The goal is to validate the
direction of the idea while effectively communicating it to
stakeholders, investors, and other audiences. Native prototyping not
only ensures user satisfaction by delivering a functional product but
also promotes efficiency and clarity in the design workflow. Investing
in this process helps designers build better products that users love,
while aligning team efforts toward a shared vision.
